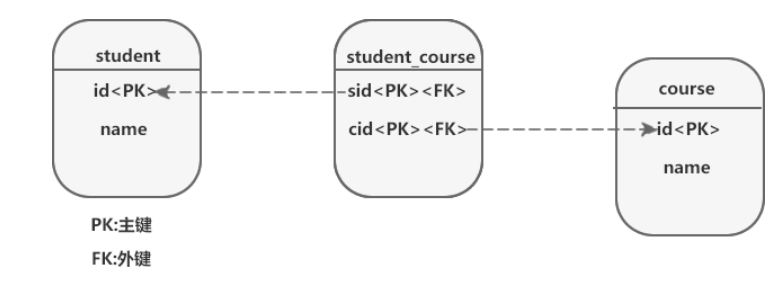
说明
本次主要针对orm中mybatis和Hibernate的关系映射进行实践
本地环境:mysql 8.0,java 1.8,idea社区版本
首先需要阅读这篇文章 介绍了对Hibernate的使用
本次实践关系映射
一对一
一对一的外键字段可以建在任何一张表中,但是,推荐建在查询频率较高 的一张表中
准备如下两个表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 create table t_idCard( id int primary key auto_increment comment '信用卡id', cardNo varchar(255) comment '信用卡编号' ); create table t_person ( id int primary key auto_increment comment '人员的id', name varchar(32) comment '人员信息', t_idCard_id int comment '信用卡id', foreign key(t_idCard_id) references t_idCard(id) );
foreign key(t_idCard_id) references t_idCard(id) 表示就是t_idCard_id是t_person的外键
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 package xyz.shi.domain; public class Person { private int id; private String name; private IdCard idCard; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public IdCard getIdCard() { return idCard; } public void setIdCard(IdCard idCard) { this.idCard = idCard; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package xyz.shi.domain; public class IdCard { private int id; private String cardNo; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getCardNo() { return cardNo; } public void setCardNo(String cardNo) { this.cardNo = cardNo; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package xyz.shi.entity; import java.util.List; public class QueryResult { private int count; // 总记录数 private List list; // 一页的数据 public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public List getList() { return list; } public QueryResult(int count, List list) { this.count = count; this.list = list; } @Override public String toString() { return "QueryResult{" + "count=" + count + ", list=" + list + '}'; } }
实体 src-man-resources-IdCard.hbm.xml对应的xml配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="xyz.shi.domain.IdCard" table="t_idCard"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="cardNo"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
实体 src-man-resources-Persion.hbm.xml对应的xml配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="xyz.shi.domain"> <class name="Person" table="t_person"> <id name="id"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name"/> <!-- 一对一配置,设置属性unique=”true”就变成了一对一 --> <!-- 配置一对一的关系,基于外键的方式 --> <many-to-one name="idCard" column="t_idCard_id" unique="true" cascade="all" ></many-to-one> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
外键有两种关联关系:
1.基于主键的方式,我这里一直失败,Persion外键idCard的值一直为空
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- 共享主键用此 (一对一关系) --> <id name="id"> <generator class="foreign"> <param name="property">idCard</param> </generator> </id> <one-to-one name="idCard" class="IdCard" constrained="true"></one-to-one> -
2.基于外键的方式,这里的cascade是级联关联,一定要加上,不然报错
cascade属性:
all :: 所有情况下均进行关联操作。
-
在 Hibernate 核心配置文件 src-man-resources-hibernate.cfg.xml 中,使用 元素来指定映射文件 Student.hbm.xml 和 Grade.hbm.xml 的位置信息,配置代码如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 配置关于数据库连接的四个项:driverClass url username password --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">123456</property> <!-- 可以将向数据库发送的SQL语句显示出来 --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化SQL语句 --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- hibernate的方言 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- 配置hibernate的映射文件所在的位置 --> <mapping resource="IdCard.hbm.xml"/> <mapping resource="Person.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 package xyz.shi.dao; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import xyz.shi.domain.Person; import xyz.shi.entity.QueryResult; import xyz.shi.utils.HibernateUtils; import java.util.List; public class PersonDao { /* * 保存 */ public void save(Person person) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); try { Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 开启事务 session.save(person); tx.commit(); // 提交事务 } catch (RuntimeException e) { session.getTransaction().rollback(); // 回滚事务 throw e; } finally { session.close(); // 关闭session } } /* * 更新 */ public void update(Person person) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); session.update(person);// 操作 tx.commit(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 删除 */ public void delete(int id) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); Object user = session.get(Person.class, id); // 要先获取到这个对象 session.delete(user); // 删除的是实体对象 tx.commit(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 根据id查询一个User数据 */ public Person getById(int id) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); Person person = (Person) session.get(Person.class, id);// 操作 tx.commit(); return person; } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 查询所有 */ public List<Person> findAll() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 方式一:使用HQL语句 // 这里的FROM User 并不是表的名字,而是User.hbm.xml中的<class name="User" 这个name List<Person> list = session.createQuery("FROM Person").list(); // 使用HQL查询 tx.commit(); return list; } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /** * 分页的查询数据列表 * @param firstResult 从结果列表中的哪个索引开始取数据 * @param maxResults 最多取多少条数据 * @return 一页的数据列表 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public QueryResult findAll(int firstResult, int maxResults) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 查询一页的数据列表 // 方式一: // Query query = session.createQuery("FROM User"); // query.setFirstResult(firstResult); // query.setMaxResults(maxResults); // List<User> list = query.list(); // 使用HQL查询 // 方式二:方法链 List<Person> list = session.createQuery( // "FROM Person") // .setFirstResult(firstResult) // .setMaxResults(maxResults) // .list(); // 查询总记录数 // session.createQuery("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM User").list().get(0); // Long count = (Long) session.createQuery("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM User").uniqueResult(); Long count = (Long) session.createQuery( // "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Person") // .uniqueResult(); tx.commit(); // 返回结果 return new QueryResult(count.intValue(), list); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import org.junit.Test; import xyz.shi.dao.PersonDao; import xyz.shi.domain.Person; import xyz.shi.domain.IdCard; import xyz.shi.entity.QueryResult; import java.util.List; public class PersonDaoTest { private PersonDao personDao = new PersonDao(); @Test public void saveTest() { // 先创建idcard IdCard idCard = new IdCard(); idCard.setCardNo("1111111"); // 创建persion Person person = new Person(); person.setName("王大伟"); person.setIdCard(idCard); personDao.save(person); } @Test public void findIdTest() { personDao.getById(16); } // 修改操作 @Test public void updateTest() { Person person = new Person(); person.setId(16); person.setName("郑1"); personDao.update(person); } // 删除操作---根据id进行删除 @Test public void deleteTest() { personDao.delete(19); } // 查询所有User @Test public void findAllTest() { List<Person> list = personDao.findAll(); for (Person user : list) { System.out.println(user); } } @Test public void findAll1() { QueryResult result = personDao.findAll(0, 5); System.out.println(result.getCount()); for (Object o : result.getList()) { System.out.println(o); } } }
一对多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 student 表为学生表,id 为学生表的主键,name 表示学生名称,gid 为学生表的外键,指向班级表的主键 id; grade 表为班级表,id 为班级表的主键,name 表示班级名称; create table grade( id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', name varchar(128) comment '班级' ); create table student( id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', name varchar(128) comment '学生名字', gid int comment '班级id', foreign key(gid) references grade(id) )comment 'gid是student表的外键';
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package xyz.shi.domain; public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; //持有实体类 Grade 的一个引用,维护多对一关系 private Grade grade; public Student() { } public Student(Integer id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Grade getGrade() { return grade; } public void setGrade(Grade grade) { this.grade = grade; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", grade=" + grade + '}'; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 package xyz.shi.domain; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Grade { private Integer Id; private String name; //持有 Student 引用的集合,来维护一对多关联关系 private Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>(); public Integer getId() { return Id; } public void setId(Integer id) { Id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Set<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(Set<Student> students) { this.students = students; } @Override public String toString() { return "Grade{" + "Id=" + Id + ", name='" + name + '}'; } }
创建 Student 的映射文件 src-man-resources-Student.hbm.xml,配置如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="xyz.shi.domain.Student" table="student" schema="shi_jdbc" lazy="true"> <!--主键映射--> <id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer"> <!--主键生成策略--> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="name" length="100" type="java.lang.String"></property> <!--维护关联关系--> <many-to-one name="grade" class="xyz.shi.domain.Grade" column="gid" cascade="all"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
注意many-to-one用法,cascade=”all”为级联关系
创建 Grade 的映射文件 src-man-resources-Grade.hbm.xml,配置如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="xyz.shi.domain.Grade" table="grade" schema="shi_jdbc"> <id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer"> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="name" length="100" type="java.lang.String"/> <!--使用 set 元素维护一对多关联关系--> <set name="students"> <key column="gid"></key> <one-to-many class="xyz.shi.domain.Student"></one-to-many> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
从 Grade(班级)的角度看,Student 和 Grade 是一对多的关系,因此 Grade 的映射文件中,需要通过 标签来维护 Grade 与 Student 的一对多关联关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 package xyz.shi.dao; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import xyz.shi.domain.Grade; import xyz.shi.domain.Person; import xyz.shi.domain.Student; import xyz.shi.entity.QueryResult; import xyz.shi.utils.HibernateUtils; import java.util.List; public class StudentDao { public void save(Student student) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); try { Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 开启事务 session.save(student); tx.commit(); // 提交事务 } catch (RuntimeException e) { session.getTransaction().rollback(); // 回滚事务 throw e; } finally { session.close(); // 关闭session } } /* * 更新 */ public void update(Student student) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); Student student1 = session.get(Student.class, student.getId()); // 设置学生信息 student1.setName(student.getName()); // 设置班级 Grade grade = student1.getGrade(); student.setGrade(grade); //我们修改了该对象的属性,并且不需要显式调用 session.saveOrUpdate(student),Hibernate 会自动将修改后的对象同步到数据库。 // session.update(student);// 操作 tx.commit(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 删除 */ public void delete(int id) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); Object user = session.get(Student.class, id); // 要先获取到这个对象 session.delete(user); // 删除的是实体对象 tx.commit(); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 根据id查询,返回对象为List object,然后直接转换到各自的实体类 */ public List<Object[]> getById(int id) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); List<Object[]> list = session.createQuery( "select s, g from Student s join s.grade g where s.id="+id).list(); tx.commit(); return list; } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /* * 查询所有 */ public List<Object[]> findAll() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); // 注意这里的用法用的原生语句,要给别名不然报错 List<Object[]> list = session.createSQLQuery("select s.id as student_id, s.name as student_name, g.id as grade_id, g.name as grade_name from student s join grade g on s.gid=g.id").list(); tx.commit(); return list; } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } /** * 分页的查询数据列表 * @param firstResult 从结果列表中的哪个索引开始取数据 * @param maxResults 最多取多少条数据 * @return 一页的数据列表 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public QueryResult findAll(int firstResult, int maxResults) { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); List<Object[]> list = session.createQuery( // "select s, g from Student s join s.grade g") // .setFirstResult(firstResult) // .setMaxResults(maxResults) // .list(); // 查询总记录数 Long count = (Long) session.createQuery( // "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Student") // .uniqueResult(); tx.commit(); // 返回结果 return new QueryResult(count.intValue(), list); } catch (RuntimeException e) { tx.rollback(); throw e; } finally { session.close(); } } }
session.createQuery( “select s, g from Student s join s.grade g”) 注意这里的用法,不支持join,s.grade其实就是Student实体类类设置的
createSQLQuery 支持用原生语句查询
一对多查询,返回List<Object[]>,然后各自的实体类去转换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import org.junit.Test; import xyz.shi.dao.StudentDao; import xyz.shi.domain.Student; import xyz.shi.domain.Grade; import xyz.shi.entity.QueryResult; import java.util.List; public class StudentDaoTest { private StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao(); @Test public void saveTest() { Grade grade = new Grade(); grade.setName("三年级"); Student student = new Student(); student.setName("王大伟"); //设置学生的班级 student.setGrade(grade); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setGrade(grade); student2.setName("小红"); studentDao.save(student); studentDao.save(student2); } @Test public void findIdTest() { List<Object[]> students = studentDao.getById(12); for (Object[] result : students) { Student student = (Student) result[0]; Grade grade = (Grade) result[1]; System.out.println(student); System.out.println(grade); } } // 修改操作 @Test public void updateTest() { Student student = new Student(); student.setId(3); student.setName("郑122"); studentDao.update(student); } // 删除操作---根据id进行删除 @Test public void deleteTest() { studentDao.delete(2); } // 查询所有 @Test public void findAllTest() { List<Object[]> list = studentDao.findAll(); for (Object[] result : list) { int studentId = (int) result[0]; String studentName = (String) result[1]; int gradeId = (int) result[2]; String gradeName = (String) result[3]; Student student = new Student(); student.setId(studentId); student.setName(studentName); Grade grade = new Grade(); grade.setId(gradeId); grade.setName(gradeName); student.setGrade(grade); System.out.println(student); System.out.println(grade); } } @Test public void findAll1() { QueryResult result = studentDao.findAll(0, 5); System.out.println(result.getCount()); List<Object[]> list = result.getList(); for (Object[] arr : list) { Student student = (Student) arr[0]; System.out.println("Student: " + student.getName() + ", Grade: " + student.getGrade().getName()); } } }
多对多
在实际的应用中,“多对多”也是一种常见的关联关系,例如学生和课程的关系,一个学生可以选修多门课程,一个课程可以被多名学生选修。
在关系型数据库中,是无法直接表达“多对多”关联关系的,我们一般会采用新建一张中间表 ,将一个“多对多”关联拆分为两个“一对多”关联解决此问题,如下图
创建如下数据表关系,图书和作者,他们是多对多的关系
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 -- 创建学生表,用上面的一对多的表即可 create table student( id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', name varchar(128) comment '学生名字', gid int comment '班级id', foreign key(gid) references grade(id) ) -- 创建课程表 create table course( id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键id', name varchar(32) comment '课程名' ); -- 建立第三张表来保存两张表的关系 create table student_course( id int primary key auto_increment comment '联表的id', student_id int comment '学生的id', course_id int comment '课程的id', foreign key(student_id) references student(id) on update cascade on delete cascade, foreign key(course_id) references course(id) on update cascade on delete cascade );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 package xyz.shi.domain; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; /** * 课程实体类 */ public class Course { private Integer id; private String name; //学生 Student 的集合作为其属性,维护多对多关联关系 private Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>(); public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Set<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(Set<Student> students) { this.students = students; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '}'; } }
修改 Student 实体类的代码,在 Student 类中以 Set 的形式引入 Course 对象作为其属性,来维护 Student 与 Course 之间的多对多关联关系,代码如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package xyz.shi.domain; .... public class Student { //将 Course 对象的集合作为其属性,以维护它们之间的多对多关联关系 private Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<>(); public Set<Course> getCourses() { return courses; } public void setCourses(Set<Course> courses) { this.courses = courses; }
创建 Course 的映射文件 src-man-resources-Coures.hbm.xml,具体配置如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping package="xyz.shi.domain"> <class name="Course" table="course" schema="jdbc"> <id name="id" column="id" > <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="name" length="100"/> <set name="students" table="student_course" cascade="save-update" inverse="true"> <key column="course_id"></key> <many-to-many class="Student" column="student_id"></many-to-many> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
inverse(反转)属性,它的作用是控制关联的双方由哪一方管理关联关系。
inverse=”true” 如果两个映射文件的inverse都设为false(默认),则会出现异常(主键重复)导致插入失败
两映射文件中的inverse都为true,则Student和Course都去维护关联关系,即同时向连接表中插入记录,则会导致主键重复而插入失败。
将其中一方的inverse设为true,让对方维持关联关系;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="xyz.shi.domain.Student" table="student" schema="shi_jdbc" lazy="true"> <!--主键映射--> <id name="id" column="id" type="java.lang.Integer"> <!--主键生成策略--> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <property name="name" column="name" length="100" type="java.lang.String"></property> <!--维护关联关系--> <many-to-one name="grade" class="xyz.shi.domain.Grade" column="gid"/> <set name="courses" table="student_course" lazy="false"> <key column="student_id"></key> <many-to-many class="xyz.shi.domain.Course" column="course_id"></many-to-many> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import org.junit.Test; import xyz.shi.dao.StudentDao; import xyz.shi.domain.Grade; import xyz.shi.domain.Student; import xyz.shi.domain.Course; import xyz.shi.entity.QueryResult; import xyz.shi.utils.HibernateUtils; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; public class StudentDao2Test { @Test public void saveTest() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); //新建学生和班级信息 Grade grade = new Grade(); grade.setName("三年级"); Student student = new Student(); student.setName("选课学生1"); student.setGrade(grade); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setName("选课学生2"); student2.setGrade(grade); grade.getStudents().add(student); grade.getStudents().add(student2); //新建三个课程 Course course = new Course(); course.setName("Java"); Course course2 = new Course(); course2.setName("PHP"); Course course3 = new Course(); course3.setName("C++"); //保存操作 session.save(student); session.save(student2); session.save(grade); session.save(course); session.save(course2); session.save(course3); //学生选课的关系相互关联 course.getStudents().add(student); student.getCourses().add(course); course2.getStudents().add(student2); student2.getCourses().add(course2); course3.getStudents().add(student2); student2.getCourses().add(course3); //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //释放资源 session.close(); } @Test public void findIdTest() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); String hql = "SELECT s, c, g FROM Student s " + "JOIN s.courses c " + "JOIN s.grade g where s.name = :name"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); query.setParameter("name", "选课学生2"); List<Object[]> students = query.list(); for (Object[] result : students) { Student student = (Student) result[0]; Course course = (Course) result[1]; Grade grade = (Grade) result[2]; System.out.println(student); System.out.println(course); System.out.println(grade); } //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //释放资源 session.close(); } // 修改操作 @Test public void updateTest() { Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); // Hibernate框架加载hibernate.cfg.xml文件 SessionFactory sessionFactory = config.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); // 相当于得到一个Connection Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); if (!tx.isActive()) { tx.begin(); } Student student = session.get(Student.class, 42); student.setName("我是谁1"); // 设置学生的班级 Grade grade = session.get(Grade.class, 2); student.setGrade(grade); Course course = session.get(Course.class, 33); // 先移除旧关联关系 for (Course existingCourse : student.getCourses()) { existingCourse.getStudents().remove(student); } // 添加新关联关系 student.getCourses().clear(); student.getCourses().add(course); course.getStudents().add(student); // 保存实体对象到数据库中 session.saveOrUpdate(student); session.saveOrUpdate(course); if (tx.isActive()) { tx.commit(); session.close(); sessionFactory.close(); } } // 删除操作 @Test public void deleteTest() { Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(); // Hibernate框架加载hibernate.cfg.xml文件 SessionFactory sessionFactory = config.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); // 相当于得到一个Connection Transaction tx = session.getTransaction(); if (!tx.isActive()) { tx.begin(); } Student student = session.get(Student.class, 40); Course course = session.get(Course.class, 31); // 移除关联关系 student.getCourses().remove(course); course.getStudents().remove(student); // 删除学生信息 session.delete(student); if (tx.isActive()) { tx.commit(); session.close(); sessionFactory.close(); } } // 查询所有 @Test public void findAllTest() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); // 根据业务来编写代码 String hql = "SELECT s, c, g FROM Student s " + "JOIN s.courses c " + "JOIN s.grade g"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); List<Object[]> students = query.list(); for (Object[] result : students) { Student student = (Student) result[0]; Course course = (Course) result[1]; Grade grade = (Grade) result[2]; System.out.println(student); System.out.println(course); System.out.println(grade); } //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //释放资源 session.close(); } @Test public void findAll1() { Session session = HibernateUtils.openSession(); Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); String hql = "SELECT s, c, g FROM Student s " + "JOIN s.courses c " + "JOIN s.grade g"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); query.setFirstResult(0); query.setMaxResults(3); List<Object[]> students = query.list(); for (Object[] result : students) { Student student = (Student) result[0]; Course course = (Course) result[1]; Grade grade = (Grade) result[2]; System.out.println(student); System.out.println(course); System.out.println(grade); } //提交事务 transaction.commit(); //释放资源 session.close(); } }
总结